How is a direct current produced ?
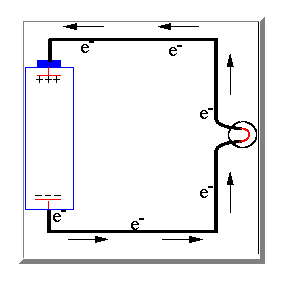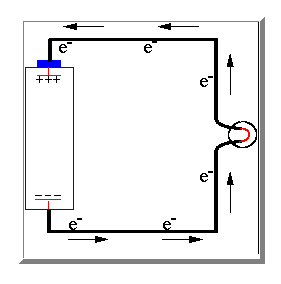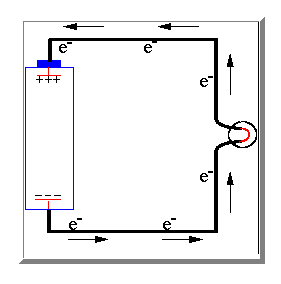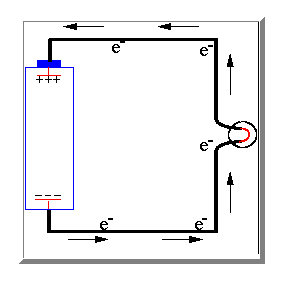
Well to explain how a direct current is produced we have to look again at the electric charges in an atom. A direct current is caused by an imbalance between these electric charges.
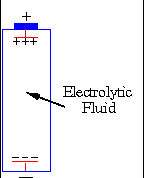
In a battery chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. Every battery
is filled with a certain chemical called an electroylite fluid and two different
types of metal. The two different types of metal have different electrical properties,
and one is connected to the negative end of the battery and the other to the
positive end. Both of these metals react differently to the electroylite fluid
and the metal connected to the negative terminal gains electrons and becomes
negatively charged while the piece of metal connected to the positive terminal
looses electrons and becomes positively charged. While the battery remains unconnected
the electrons on the negative terminal cannot reach the positive terminal.

If the two terminals of the battery are connected together electrons are then
able to pass long the wire from the negative terminal to the positive terminal
to attempt to balance the electrical charge. As the electrons move through the
wire they loose energy and this energy turns into heat. Since the energy that the electrons have comes from chemical energy
in the electroylite eventually the chemical energy runs out and the battery
becomes flat. This is a direct current.